Custom Fields
Custom fields are available on Enterprise plans.
Custom fields were introduced in Flagsmith 2.116.0.
This guide explains how to define and manage custom fields in Flagsmith. Custom fields allow you to store additional, relevant information alongside Flagsmith entities such as flags, segments, or environments. You can use them to:
- Relate every flag to a ticket in your issue tracker so that everyone knows what a flag does and what state of development it is in.
- Add a link from Flagsmith segments to the corresponding segments in your analytics platform.
- Add a detailed description to your Flagsmith environments.
You can define custom fields that are shown when creating or modifying flags, segments or environments. Custom fields are defined per organisation.
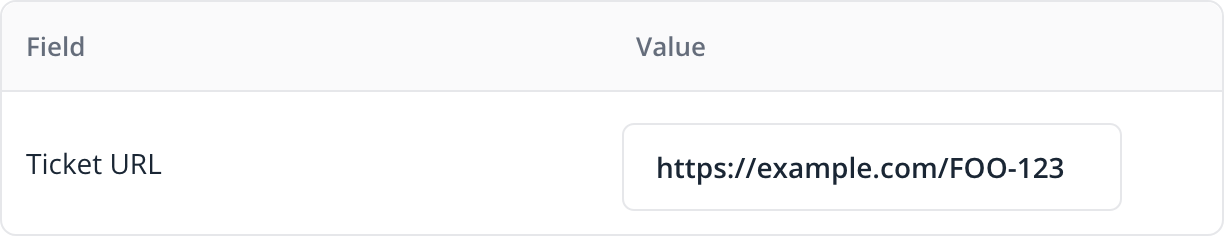
The following screenshot shows a custom field named "Ticket URL" that is displayed to Flagsmith users when editing or creating a feature:
Prerequisities
- To define custom fields, you must have administrator permissions for the relevant project.
- To update the values of custom fields, you must have edit permissions for the specific entity.
Define custom fields
Follow these steps to define a custom field:
- Navigate to Organisation Settings.
- Select Custom Fields.
- Click on the option to create a new custom field.
- A custom field can have the following properties:
- Name: the visible name of the field as it will be presented to users.
- Description: a short description of what the field is for. It is only shown when editing custom field definitions.
- Type: validates this field's data when saving to be one of the following types:
- String: A single line of text.
- Multi-line string: One or more lines of text.
- Integer: Whole numbers without a decimal point.
- Boolean: A binary choice between true or false.
- URL: An absolute URL with an explicit scheme as defined by Python's
urlparse function. For example,
https://flagsmith.comis considered valid but/example/foois not.
- Entities: Which Flagsmith entities to display these fields for during creation or editing. The following options
are allowed:
- Features
- Segments
- Environments
- Required: Lets you choose whether a field is required for each entity it is associated with. For example, you could make a ticket URL required for features but optional for segments.
Modify Existing Fields
Field data types are only validated when saving. Modifying existing field data types will not delete or modify existing data.
Changing an optional field into a required field will prevent you from creating or updating the relevant entities without providing a value for that field.
Deleting custom fields will also delete all data associated with that field.
Consume custom fields
Custom fields are mainly intended to be read by humans visiting the Flagsmith dashboard, typically for traceability or accountability purposes.
Custom field values associated with features belong to the features themselves, and not an environment's feature state; you cannot override custom field values in different environments, segments or identities. They are not returned to applications that consume flags.
Custom field values are added directly to the metadata field of the entity they are defined in, which can be read using the Flagsmith Admin API. For example, to fetch a feature's custom fields, use the endpoint to fetch a feature by ID:
curl "https://api.flagsmith.com/api/v1/projects/YOUR_PROJECT_ID/features/YOUR_FEATURE_ID/" \
-H "Authorization: Api-Key YOUR_API_KEY"
This returns information about the feature itself, including metadata which contains the custom field values:
{
...
"metadata": [
{
"id": 123,
"model_field": 128,
"field_value": "https://example.com/FOO-123"
},
{
"id": 124,
"model_field": 129,
"field_value": "Example Team"
}
]
}
To fetch the field definitions themselves, use the endpoint to fetch metadata model fields. For example:
curl "https://api.flagsmith.com/api/v1/organisations/YOUR_ORGANISATION_ID/metadata-model-fields/ \
-H "Authorization: Api-Key YOUR_API_KEY"
This returns the definition of each custom field:
{
"count": 2,
"next": null,
"previous": null,
"results": [
{
"id": 178,
"name": "Ticket URL",
"type": "url",
"description": "URL to ticket in our issue tracker",
"organisation": 15467
},
{
"id": 179,
"name": "Product code",
"type": "int",
"description": "Product code associated with this feature",
"organisation": 15467
}
]
}